Inflation, the persistent increase in the overall price level of goods and services, is a matter of great significance for central banks worldwide. As the central bank of the United Kingdom, the Bank of England (BoE) plays a pivotal role in handling inflation and ensuring price stability within the country. This article provides an extensive analysis of the strategies employed by the BoE, the challenges it encounters while managing inflation, and explores potential future developments in inflation management.
The BoE’s Strategies in Inflation Management
To effectively manage inflation, the BoE utilizes a diverse range of strategies and tools. One of its primary instruments is monetary policy, specifically the regulation of interest rates. By adjusting the base interest rate, commonly known as the Bank Rate, the BoE influences the cost of borrowing for banks, businesses, and consumers. Through changes in interest rates, the BoE aims to stimulate or restrain economic activity, thereby impacting inflationary pressures. Higher interest rates can reduce borrowing and spending, thus curbing inflation, while lower rates can encourage borrowing and promote economic expansion.
In addition to interest rate adjustments, the BoE employs forward guidance as a communication tool. Forward guidance involves providing information to the public and financial markets about the future direction of monetary policy. This guidance influences expectations regarding interest rates, thereby shaping borrowing and investment decisions. By offering clarity on the BoE’s policy intentions, forward guidance can anchor inflation expectations and contribute to price stability.
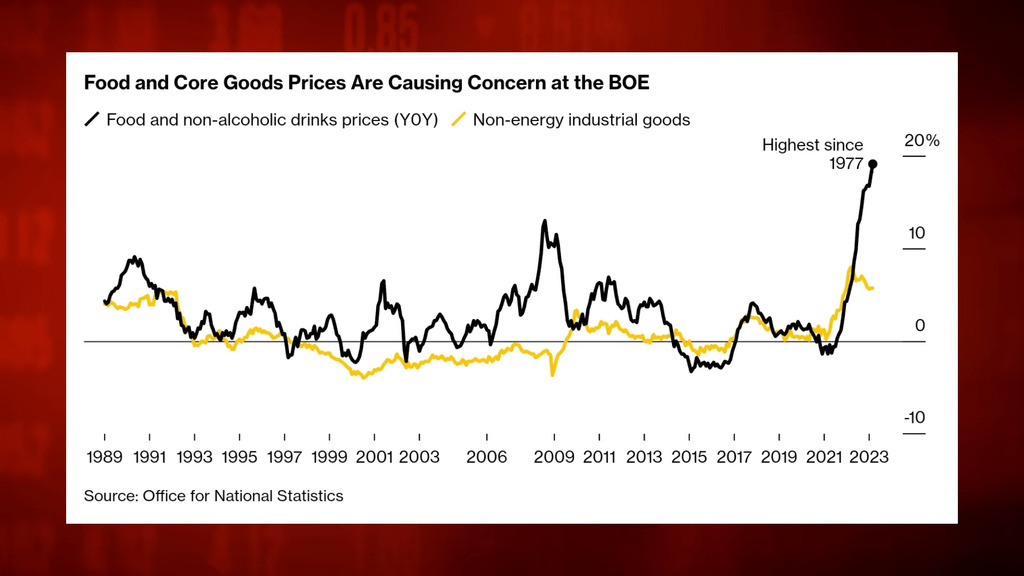
Challenges in Inflation Management
The Bank of England faces several challenges in its endeavor to effectively manage inflation. These challenges include:
External Factors: External events and factors beyond the control of the BoE can significantly impact inflation. Global economic conditions, fluctuations in exchange rates, geopolitical tensions, and shocks in commodity prices can all influence inflationary pressures. The BoE must carefully analyze and respond to these external factors to mitigate their effects on domestic inflation.
Trade-Offs between Inflation and Growth: Balancing inflation control with economic growth poses a significant challenge. Implementing aggressive measures to combat inflation, such as raising interest rates, may slow down economic activity and increase unemployment. On the other hand, prioritizing growth over inflation control can lead to overheating and exacerbate inflationary pressures. Policymakers at the BoE must skillfully navigate this trade-off to ensure price stability while supporting sustainable economic expansion.
Structural Factors: Long-term structural factors can influence inflation dynamics. Technological advancements, demographic changes, and shifts in global supply chains all impact the relationship between prices, wages, and production costs. The BoE needs to consider these structural factors in its inflation management strategies to accurately anticipate and respond to inflationary pressures.
Fiscal Policy Coordination: The interaction between monetary policy conducted by the BoE and fiscal policy implemented by the UK government can affect inflation outcomes. Close coordination and communication between the BoE and fiscal authorities are crucial to avoid conflicts or inconsistencies in policy objectives. Ensuring alignment and a coherent approach to inflation management is essential to maintain price stability and support sustainable economic growth.
The BoE’s Response to the Mortgage Problem
The topic focuses on the response of the Bank of England (BoE) to the mortgage problem in the UK. The mortgage market in the UK is different from other countries because it has a substantial number of variable-rate mortgages that are tied to the BoE’s policy rates. This presents a unique challenge for the BoE when it comes to managing inflation.
In order to control inflation, the BoE may decide to raise interest rates. However, this action can have consequences for borrowers who have variable-rate mortgages. When interest rates increase, the mortgage costs for these borrowers also go up. This can potentially affect their financial well-being and have an impact on the overall housing market.
Therefore, the BoE needs to find a delicate balance between managing inflation and minimizing the negative effects on borrowers. This requires careful consideration of the potential consequences of interest rate changes and effective communication with market participants, such as lenders, borrowers, and other stakeholders in the mortgage market.
By effectively communicating its decisions and the rationale behind them, the BoE can help market participants better understand the reasons for interest rate adjustments. This transparency can help reduce uncertainty and enable borrowers to make informed decisions regarding their mortgages. It also allows lenders to manage their portfolios effectively and make necessary adjustments to accommodate changes in interest rates.
Coordination with International Central Banks
Coordination with international central banks is of utmost importance for the Bank of England, given its operation within a globally interconnected financial system. In this era of globalization, economic interdependencies among nations have reached unprecedented levels. Consequently, the decisions made by major central banks worldwide can have far-reaching implications for the UK economy.
One significant example of such coordination is the relationship between the Bank of England and the US Federal Reserve. The monetary policy decisions taken by the Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, can create spillover effects that reverberate throughout the global economy. These effects can manifest in various ways, including exchange rate fluctuations, capital flows, and alterations in financial market conditions.
When the Federal Reserve tightens or loosens its monetary policy, it can influence interest rates, which, in turn, affect borrowing costs and investment decisions. Such changes have the potential to impact the UK economy through their effects on trade, investment flows, and overall economic activity. For instance, if the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it may attract capital from the UK to the US, leading to a depreciation of the British pound and potentially affecting the competitiveness of UK exports.
To mitigate and manage the potential repercussions of global monetary policy decisions, the Bank of England engages in ongoing coordination efforts with international central banks. By maintaining open lines of communication and sharing insights and perspectives, central banks can better understand the implications of their respective policies and collectively work towards achieving stability and sustainable growth.
One key area of focus for coordination is inflation management. Central banks around the world strive to maintain price stability by targeting a specific inflation rate. However, achieving this goal requires a coherent and synchronized approach among central banks. If one central bank takes actions that create significant deviations in inflation expectations, it can impact global financial stability and create challenges for other central banks in meeting their objectives.
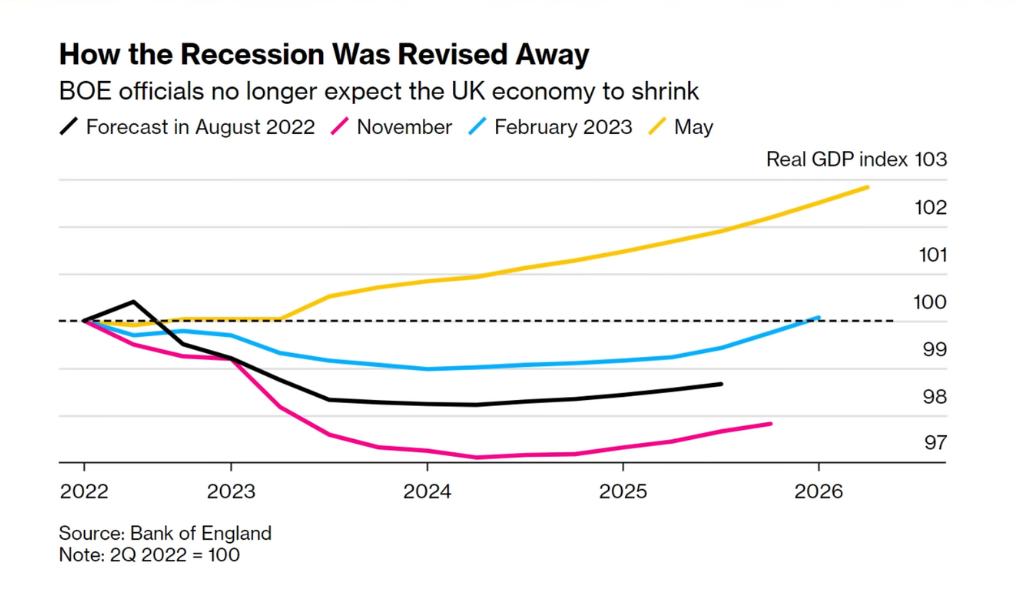
Evolving Inflation Outlook
Accurate forecasting plays a crucial role in effective inflation management. The BoE regularly provides inflation forecasts, which serve as important guidance for businesses, households, and financial market participants. However, the BoE has faced criticism for the volatility and revisions in its inflation forecasts, which can undermine public and market confidence. Enhancing the accuracy of inflation forecasting requires robust economic models, advanced data analysis techniques, and improved communication of assumptions and uncertainties underlying the forecasts. The BoE must strive to enhance its forecasting capabilities to provide more reliable guidance to the public and market participants.
Technological Advancements and Inflation Management
Technological advancements, including artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analytics, present opportunities to enhance inflation management. AI can process vast amounts of economic data, identify patterns, and generate more accurate inflation forecasts. It can assist policymakers in understanding complex relationships between economic variables, identifying emerging risks, and formulating effective policy responses. However, the integration of AI in inflation management requires careful consideration of ethical and transparency issues, as well as addressing potential biases in algorithms and data quality. The BoE needs to develop robust governance frameworks and invest in technological capabilities to leverage the benefits of AI while ensuring its responsible and effective use.
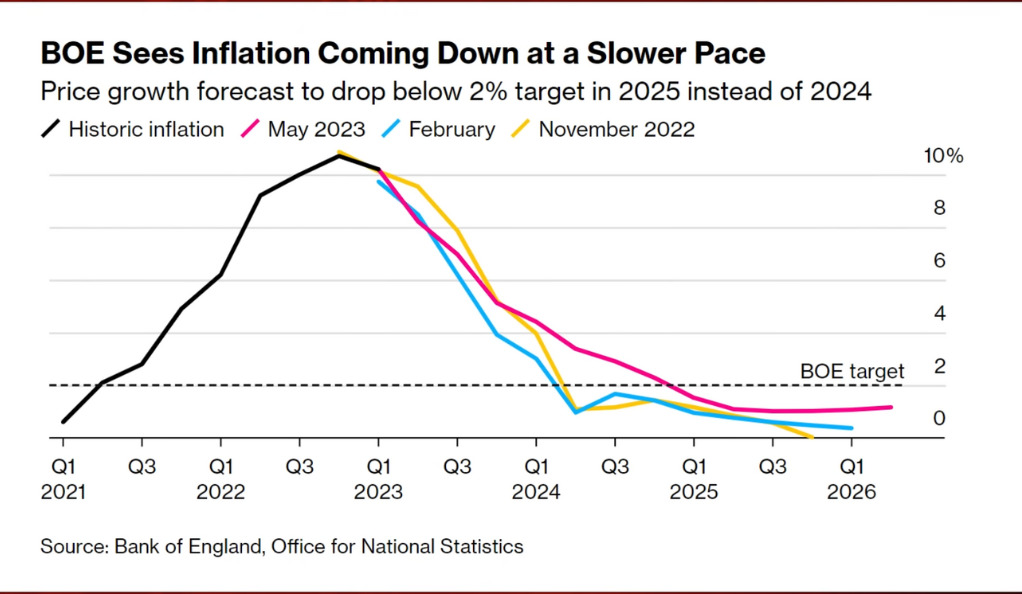
Future Outlook and Considerations
In the future, the Bank of England will encounter a constantly changing and unpredictable environment when it comes to managing inflation. The bank will have to be flexible and responsive to evolving economic circumstances, geopolitical changes, and advancements in technology. It will also need to take into account emerging risks, particularly those related to climate change and digitalization, as these factors can significantly impact inflation patterns.
Climate change poses a unique challenge for the Bank of England, as it can influence the overall economic landscape and potentially affect inflation dynamics. Environmental factors, such as extreme weather events, natural resource scarcity, or shifts in agricultural productivity, can disrupt supply chains and lead to price fluctuations. The bank will need to closely monitor and assess the potential effects of climate change on inflation and develop appropriate strategies to mitigate these risks.
Furthermore, digitalization and technological advancements will continue to shape the economy and have implications for inflation management. The rapid growth of digital technologies, automation, and artificial intelligence can alter production processes, labor markets, and consumer behavior. The Bank of England will need to understand and anticipate these changes in order to effectively gauge their impact on inflation and adjust its policies accordingly.
To navigate this complex environment, it is crucial for the Bank of England to engage with various stakeholders. This includes businesses, households, and academic experts who can provide diverse perspectives and insights. By actively seeking input from these stakeholders, the bank can ensure that its inflation management strategies align with the needs of the economy and society as a whole.
Conclusion
The management of inflation by the Bank of England requires a proactive and multifaceted approach. The BoE employs various strategies, including interest rate adjustments and forward guidance, to maintain price stability and support economic growth. However, challenges arise from external factors, trade-offs between inflation and growth, structural changes, fiscal policy coordination, and the unique characteristics of the UK’s mortgage market. Effective coordination with international central banks, accurate inflation forecasting, and the responsible integration of technological advancements are critical for the BoE’s future success in inflation management. By addressing these challenges and embracing opportunities, the Bank of England can contribute to a stable and prosperous economic future for the United Kingdom.
Ainu Token aims to offer impartial and trustworthy information on cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and shares. However, we don't provide financial advice and recommend users to conduct their own studies and thorough checks.



Comments (No)