The banking world is currently grappling with a crisis that has drawn comparisons to the 2008 financial meltdown. Unlike that global catastrophe, this crisis is more localized, affecting only a handful of banks. However, its repercussions are being felt across the financial landscape, raising concerns and drawing attention from regulators, financial experts, and the public. This article will delve into the various facets of the current banking crisis, exploring its origins, impact, and potential future consequences.

Comparison with the 2008 Crisis
The 2008 financial crisis was a global phenomenon that shook the very foundations of the world economy. It led to widespread panic, massive bailouts, and long-lasting economic repercussions. In contrast, the current banking crisis is more limited in scope, affecting only a select few banks. However, the comparison with the 2008 crisis is inevitable, given the magnitude of the impact that crisis had on the global economy.
While the current crisis is not as widespread, it has raised similar concerns about the stability and integrity of the financial system. The failure of a few banks has led to questions about the overall health of the banking sector and the effectiveness of regulatory oversight. The lessons learned from the 2008 crisis are being revisited, and there is a renewed focus on ensuring that the mistakes of the past are not repeated.
The current crisis has also brought to the fore the role of large financial institutions and their influence on the broader economy. The acquisition of failing banks by larger entities, such as JP Morgan Chase, has raised questions about concentration of power and the potential risks associated with “too big to fail” institutions.
The Decline in Deposits
One of the most alarming aspects of the current crisis is the significant decline in deposits. At the end of the last quarter, there was a 41% decline in deposits compared to the previous quarter. The $104 billion reported was below analyst estimates, indicating a lack of confidence in the banking sector.
This decline in deposits is not just a statistical anomaly; it reflects a broader trend of uncertainty and mistrust in the banking system. Depositors are increasingly wary of the stability of their banks, leading to a flight of capital to perceived safer havens. This has put additional pressure on banks, leading to liquidity challenges and further undermining confidence in the system.
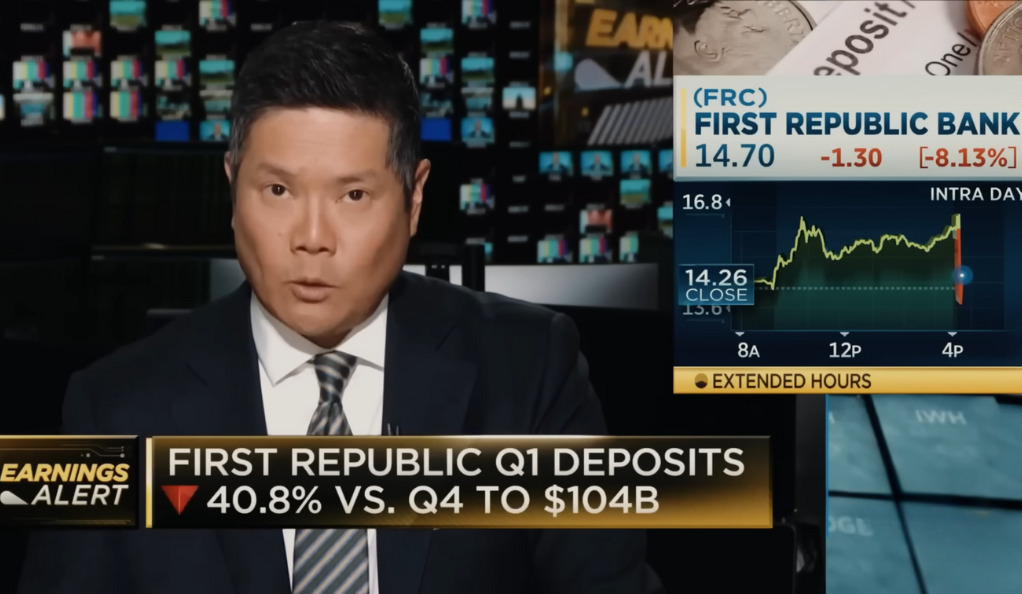
The decline in deposits also has broader economic implications. Banks play a crucial role in the economy by providing credit and facilitating investment. A decline in deposits can lead to a credit crunch, hampering economic growth and leading to a vicious cycle of declining confidence and economic stagnation.
The response to this decline has been swift, with a consortium of large U.S. banks stepping in to shore up the deposit base at First Republic. However, this intervention has raised questions about the long-term stability of the banking system and the need for more robust regulatory oversight.
The Role of the Consortium of Large U.S. Banks
In response to the crisis, a consortium of large U.S. banks put in $30 billion to shore up the deposit base at First Republic. This move was seen as a necessary step to stabilize the bank and prevent further losses.
The consortium’s intervention highlights the interconnectedness of the banking system and the importance of collaboration in times of crisis. It also underscores the influence and responsibility of large financial institutions in maintaining stability in the financial system.

However, this intervention has also raised concerns about the concentration of power in the hands of a few large banks. The ability of a small group of banks to influence the fate of a failing institution raises questions about competition, fairness, and the potential risks associated with such concentration of power.
The role of the consortium also highlights the importance of regulatory oversight and the need for clear rules and guidelines to govern the behavior of large financial institutions. The intervention may have been necessary, but it also raises questions about the adequacy of existing regulations and the need for more robust oversight to prevent future crises.
Job Cuts at First Republic Bank
The crisis has also led to job cuts at First Republic Bank. The bank announced that it will cut 20 to 25 percent of its workforce in the current quarter, a move that underscores the severity of the situation.
Job cuts are a common response to financial challenges, but they also have broader social and economic implications. The loss of jobs leads to a decline in consumer spending, further hampering economic growth. It also raises questions about the social responsibility of banks and the need for measures to protect employees and communities affected by financial crises.
The job cuts at First Republic Bank also highlight the human cost of financial instability. Behind the numbers and statistics are real people whose lives are affected by the decisions made by banks and regulators. This underscores the importance of responsible management and the need for a balanced approach that considers not just the bottom line but also the broader social impact.

Regulatory Repercussions
The banking crisis is expected to have regulatory repercussions for years to come. The failure of a few banks has exposed weaknesses in the regulatory framework and highlighted the need for more robust oversight.
Regulators are now faced with the challenge of balancing the need for stability with the need for innovation and competition. Overly strict regulations can stifle growth and hinder the ability of banks to adapt to changing market conditions. However, lax oversight can lead to irresponsible behavior and increase the risk of financial instability.
The current crisis has also brought to the fore the importance of international cooperation in regulatory matters. The interconnectedness of the global financial system means that a crisis in one country can quickly spread to others. Coordinated regulatory action is essential to prevent the spread of financial instability and ensure that the lessons learned from past crises are applied globally.
However, experts urge regulators to be careful with rule changes to avoid exacerbating the situation. Hasty or ill-considered regulations can lead to unintended consequences and further undermine confidence in the system. A thoughtful, measured approach that considers the long-term stability of the financial system is essential.

Bank Failures and JP Morgan’s Role
The failure of First Republic Bank and its subsequent acquisition by JP Morgan Chase is a significant development in the current crisis. JP Morgan often emerges as a winner in crises, but the terms of the deal have raised questions.
The acquisition highlights the role of large financial institutions in shaping the financial landscape. JP Morgan’s willingness to step in and acquire a failing bank underscores its influence and the importance of large banks in maintaining stability in the financial system.
However, the terms of the deal have been criticized as overly favorable to JP Morgan. The acquisition included a $50 billion loan from the FDIC, raising questions about the appropriateness of such a large government-backed loan to a private institution.
Critics also argue that the deal sets a dangerous precedent, encouraging risky behavior by banks with the expectation that they will be bailed out by larger institutions or the government. This “moral hazard” can lead to irresponsible behavior and increase the risk of future crises.
The role of JP Morgan also raises questions about the concentration of power in the hands of a few large banks. The ability of a single institution to influence the fate of a failing bank highlights the potential risks associated with such concentration and the need for more robust regulatory oversight.

Deal Details and Criticism
The deal, in which JP Morgan acquired First Republic Bank’s assets, including a $50 billion loan from the FDIC, has been criticized. Critics argue that the terms are overly favorable to JP Morgan and accuse the bank of predatory behavior.
The acquisition included not just the assets of First Republic Bank but also significant government support in the form of loans and protections. This has led to accusations that the deal amounts to a government-backed bailout of a private institution, raising questions about the appropriateness of such intervention.
Critics also argue that the deal undermines competition by allowing a large bank to acquire a failing competitor at a bargain price. This concentration of power in the hands of a few large banks can stifle competition and hinder innovation, leading to a less dynamic and resilient financial system.
The deal also highlights the importance of transparency and accountability in the financial system. The terms of the deal were not publicly disclosed, leading to speculation and uncertainty. This lack of transparency undermines confidence in the system and highlights the need for clear rules and guidelines to govern such transactions.
Impact on the Federal Reserve (FED)
The banking crisis has put pressure on the FED, which now faces a dilemma between combating inflation and preventing further financial collapses. The decisions the FED makes in response to this crisis could have far-reaching consequences.
The FED’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability and promote economic growth. However, the current crisis has created a complex and challenging environment in which to achieve these goals.

On the one hand, the FED must consider the impact of inflation on the economy and take measures to keep prices in check. On the other hand, it must also consider the impact of its actions on the stability of the financial system and the potential risks associated with tightening monetary policy in a fragile economic environment.
The FED’s decisions will have a direct impact on interest rates, credit availability, and overall economic growth. A misstep in either direction could lead to further instability and undermine confidence in the FED’s ability to manage the economy.
The FED’s actions will also have international implications, as changes in U.S. monetary policy can affect global financial markets and economic conditions. Coordinated action with other central banks and international institutions may be necessary to prevent the spread of financial instability and ensure a coordinated response to the crisis.
Stagflation Concerns
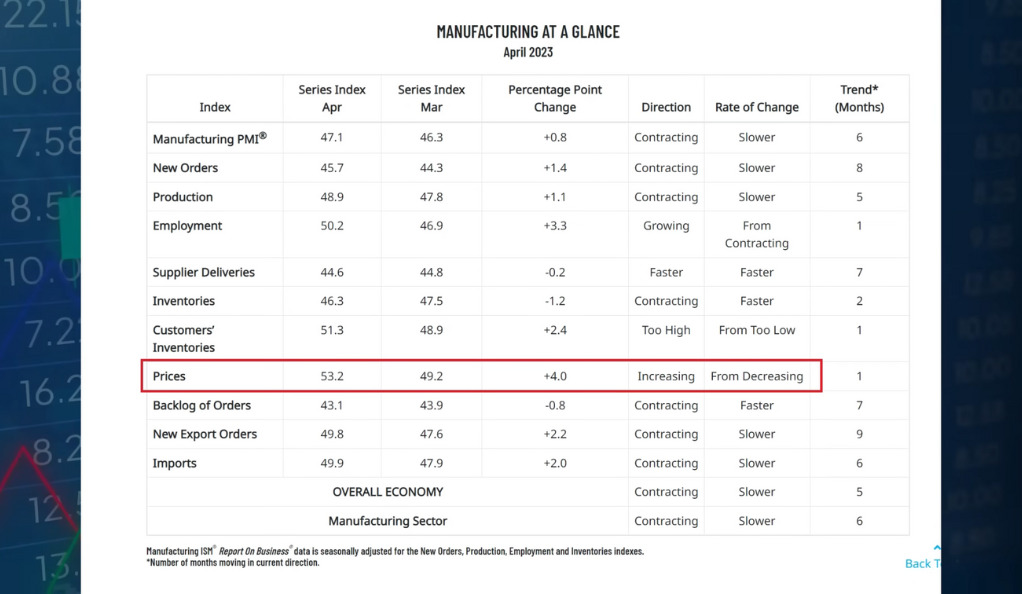
There are concerns about stagflation, with signs of higher inflation and weak growth. The ISM Manufacturing Index shows increasing prices, suggesting that inflation could rebound.
Stagflation is a complex and challenging economic phenomenon characterized by stagnant economic growth, high unemployment, and rising inflation. It presents a unique challenge to policymakers, as traditional tools to combat inflation (such as raising interest rates) can exacerbate economic stagnation, while measures to stimulate growth (such as lowering interest rates) can fuel inflation.
The current signs of stagflation are particularly concerning given the fragile state of the global economy. The COVID-19 pandemic has already taken a significant toll on economic growth, and the banking crisis has added further uncertainty.
The potential for stagflation also raises questions about the effectiveness of current monetary and fiscal policies. Traditional tools may be less effective in combating stagflation, and innovative approaches may be needed to navigate this complex economic landscape.
The potential for stagflation also highlights the importance of coordinated action at the international level. Stagflation is not just a domestic concern; it can have global implications, affecting trade, investment, and overall economic stability. International cooperation and coordination will be essential to address this challenge and prevent the spread of economic instability.
Potential Consequences of FED Decisions
If the FED either doubles down on combating inflation or backs off, it could lead to more financial instability. The decisions the FED makes now will have long-term implications for the economy.
Doubling down on combating inflation could lead to higher interest rates and tighter credit conditions. While this may help to keep inflation in check, it could also lead to a slowdown in economic growth and further strain on the banking system. Higher interest rates can lead to a decline in borrowing and investment, hampering economic growth and leading to job losses and financial instability.

Backing off and adopting a more dovish stance could have the opposite effect. Lower interest rates and more accommodative monetary policy could stimulate growth and ease pressure on the banking system. However, it could also fuel inflation, leading to a loss of purchasing power and undermining confidence in the currency.
The FED’s decisions will also have international implications, as changes in U.S. monetary policy can affect global financial markets and economic conditions. The interconnectedness of the global economy means that the FED’s actions will have ripple effects, affecting trade, investment, and overall economic stability.
The FED’s decisions will also be closely watched by financial markets, and any perceived missteps could lead to volatility and uncertainty. Clear communication and transparency will be essential to manage expectations and maintain confidence in the FED’s ability to navigate this complex economic landscape.
Debt Limit Deadline
U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen’s announcement of a new debt limit deadline of June 1st highlights the government’s financial constraints and adds another layer of complexity to the situation.
The debt limit is a legal cap on the amount of money the federal government can borrow to pay its bills. Reaching the debt limit without an agreement to raise it can lead to a default on government obligations, with potentially catastrophic consequences for the global economy.
The current debt limit deadline adds to the uncertainty and complexity of the economic environment. It raises questions about the government’s ability to respond to the banking crisis and the potential impact on fiscal policy.
The debt limit also highlights the broader challenges facing the U.S. economy, including rising debt levels, fiscal constraints, and the need for responsible budgeting. The decisions made in response to the debt limit will have long-term implications for the country’s fiscal health and economic stability.
The debt limit also underscores the importance of political cooperation and the need for bipartisan solutions to complex economic challenges. Political gridlock and partisan bickering can exacerbate economic uncertainty and undermine confidence in the government’s ability to manage the economy.

General Criticism of the Banking System
Throughout the crisis, there has been strong criticism towards the banking system, JP Morgan Chase, and the government’s handling of the situation. Accusations of money laundering, predatory behavior, and mismanagement have been leveled against these entities.
The criticism reflects a broader distrust of the financial system and a perception that large financial institutions are acting in their own interests at the expense of the broader public. This perception has been fueled by the terms of the deal between JP Morgan and First Republic Bank, as well as the perceived lack of transparency and accountability in the system.
The criticism also highlights the importance of public trust in the financial system. Without trust, the system cannot function effectively, and the lack of confidence can lead to a flight of capital, further undermining stability.
The criticism also underscores the need for more robust regulatory oversight and the importance of transparency and accountability in the financial system. Clear rules, effective enforcement, and transparent decision-making are essential to rebuild trust and ensure the long-term stability of the financial system.
Conclusion
The current banking crisis is a complex and multifaceted challenge that has exposed weaknesses in the financial system and raised questions about the effectiveness of regulatory oversight. The crisis has also highlighted the interconnectedness of the global economy and the importance of coordinated action to prevent the spread of financial instability.
The response to the crisis will have long-term implications for the economy, the financial system, and the broader society. The decisions made now will shape the future of the financial system and determine the path forward for the global economy.
The crisis also underscores the importance of trust, transparency, and accountability in the financial system. Without these foundational elements, the system cannot function effectively, and the lack of confidence can lead to further instability.
As we navigate this complex landscape, we must be mindful of the lessons of the past and the need for a balanced approach that considers not just the bottom line but also the broader social impact. The decisions we make now will shape the future of our economy and our society, and we must approach them with care, thoughtfulness, and a commitment to the greater good.
Ainu Token aims to offer impartial and trustworthy information on cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and shares. However, we don't provide financial advice and recommend users to conduct their own studies and thorough checks.


Comments (No)