In the dynamic world of trading, timing is everything. One of the most profitable strategies that seasoned traders swear by is trading reversals. This strategy involves identifying the exact moment the price changes direction, allowing traders to capitalize on these shifts. This approach can lead to high risk-reward ratios and significant profits. But how exactly does it work? What are the key elements to consider? Let’s delve deeper into this fascinating strategy.
Understanding Reversals
Reversals are a trader’s dream. They represent the precise point where the price changes direction. Imagine being able to snipe that exact moment, not only would you be getting insane risk-reward ratios, but you’d also be making a ton of profit on top of it. It’s like catching a wave just as it turns, riding it all the way to the shore. This strategy works for everything – stocks, Forex, crypto – it doesn’t matter. And the even cooler thing is that it works on all time frames.
The Concept of Liquidity Grab
A liquidity grab is a market phenomenon that occurs when the price of an asset breaks a support or resistance level and then reverses direction. It’s akin to a feint in a boxing match, where a boxer tricks their opponent with a deceptive move before delivering the knockout punch.
In trading terms, imagine a scenario where the price of an asset breaks a resistance level, indicating a potential upward trend. Many traders, expecting the price to continue rising, will enter long positions. However, if this break is a liquidity grab, the price will instead reverse and start moving downwards.

The Role of Liquidity Grab in Trading Strategy
The liquidity grab plays a crucial role in trading strategies, particularly those involving reversals. This is because a liquidity grab adds fuel to the reversal. When the price reverses after a liquidity grab, it triggers the stop losses set by traders who had entered long positions. This leads to a strong impulsive movement in the opposite direction, which traders using a reversal strategy can capitalize on.
Liquidity Grab and Market Psychology
The concept of a liquidity grab is deeply rooted in market psychology. When the price breaks a support or resistance level, it creates an illusion of a continuing trend, leading many traders to enter positions in line with this perceived trend. However, when the price reverses, these traders are caught off guard, leading to a rush to exit their positions and a sharp price movement in the opposite direction.
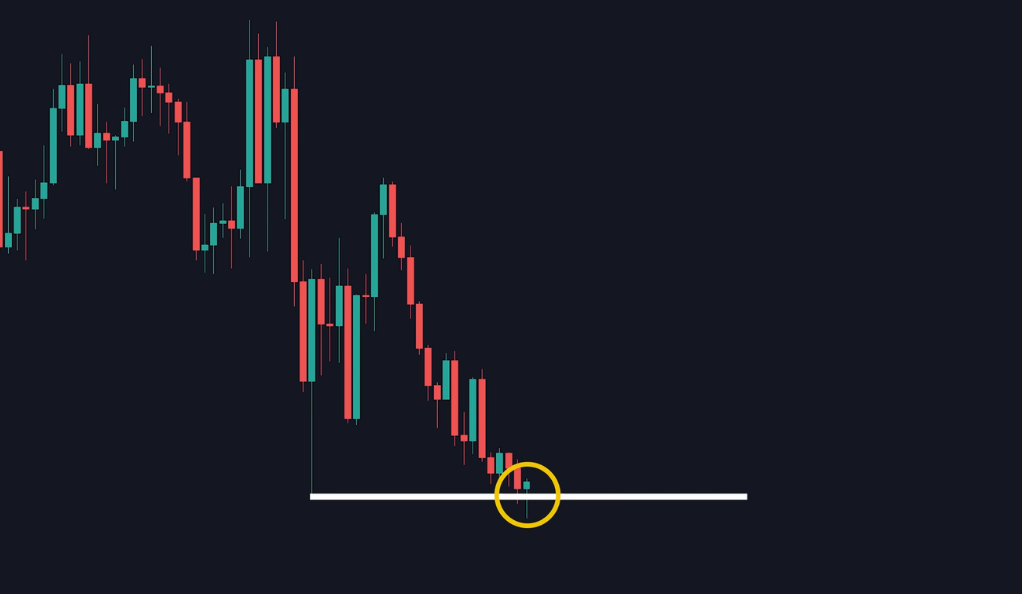
Identifying a Liquidity Grab
Identifying a liquidity grab can be challenging, as it requires a keen understanding of price action and market dynamics. Traders need to closely monitor support and resistance levels and watch for sudden price reversals. Some traders also use technical indicators to help identify potential liquidity grabs.
Marking Your Entry Point
Now, where do you jump in? The entry point for a trade is marked at the candle that made the liquidity grab. It’s like finding the exact bottom or top of a move, leading to large profits and small losses. It’s akin to finding the perfect spot to dive into a swimming pool – not too shallow, not too deep. The entry is pretty simple, you are going to mark your entry point at the candle that made the liquidity grab.
The Importance of Risk-Reward Ratio
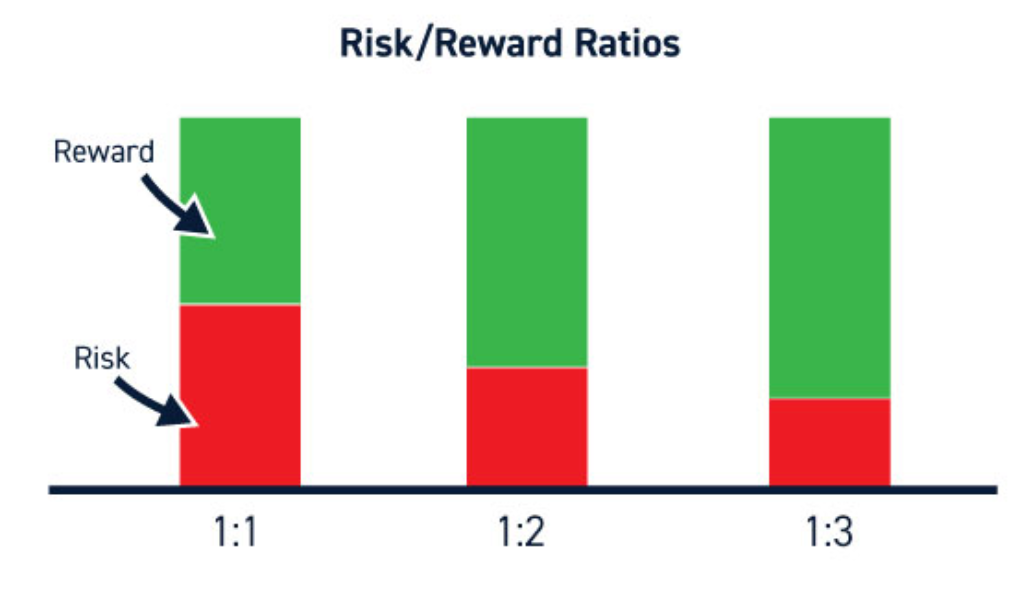
The risk-reward ratio is a simple yet powerful concept. It’s akin to planting a seed and nurturing it to grow into a tree. The initial effort and resources you put into planting and caring for the seed represent the risk. In contrast, the fruits that the tree eventually bears symbolize the reward.
In trading terms, the risk is the amount of money you’re willing to lose on a trade, while the reward is the profit you aim to make. The risk-reward ratio is calculated by dividing the potential loss (risk) of a trade by the potential profit (reward).
The Role of Risk-Reward Ratio in Trading Strategy
The risk-reward ratio plays a crucial role in any trading strategy. It helps traders manage their risks and potential profits effectively. A good risk-reward ratio ensures that even if a trade results in a loss, the loss is small compared to the potential profit if the trade is successful.
This concept is what makes strategies like trading reversals so successful. In reversal trading, the risk-reward ratios can be absolutely insane because you are finding the exact bottom or top of the move. This means that your potential profit (reward) is significantly larger than your potential loss (risk), leading to a favorable risk-reward ratio.
Balancing Risk and Reward
Balancing risk and reward is a delicate act. It’s about finding the sweet spot where the potential profit outweighs the potential loss, but not by so much that the trade becomes too risky. This balance is not always easy to achieve, and it requires a deep understanding of the market and the specific asset you’re trading.
The Impact of Risk-Reward Ratio on Trading Success
A favorable risk-reward ratio can significantly impact a trader’s success. It can help traders stay profitable in the long run, even if they have more losing trades than winning ones. This is because the profits from the winning trades, due to the favorable risk-reward ratio, can offset the losses from the losing trades.
Improving Your Strategy
No strategy is perfect, but there are ways to improve it. Look for liquidity grabs with peaks closer together, add confluences like divergences, and identify reversals at the bottoms or tops of big moves. It’s like fine-tuning a musical instrument, getting it to play the perfect note. The back test results suggest that if the liquidity grab and the entry candle were closer than 10 candles apart, the drop was a lot larger compared to the peaks further apart.
The Magic of Indicators
In the digital age, why not let technology lend a hand? The author mentions a private indicator that automatically finds liquidity grabs and entries, saving time and effort. It’s like having a personal assistant, always ready to help. This strategy performs so well that it has been added to the indicator. The indicator will automatically find everything for you – it’ll find the liquidity grab, mark the entry point, and will also tell you exactly when to enter.
The Risks of Trading
Trading, like any financial endeavor, carries inherent risks. While the potential for profit can be alluring, it’s crucial to remember that losses are also a part of the game. Just as one wouldn’t hit the highway without first learning to drive in a safe environment, it’s essential to thoroughly understand and test a trading strategy before using it. This article aims to delve deeper into the risks associated with trading.

Understanding Trading Risks
Trading involves buying and selling financial instruments, such as stocks, commodities, or currencies, with the aim of making a profit. However, the markets can be unpredictable, and there are no guarantees of making a profit. In fact, it’s possible to lose a significant portion, or even all, of your initial investment.
Market risk, also known as systematic risk, is the risk that the value of a portfolio will decrease due to changes in market factors. These factors can include economic indicators, such as interest rates and inflation, as well as geopolitical events and natural disasters. Market risk is inherent in all investments and cannot be eliminated through diversification.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that a trader may not be able to buy or sell a financial instrument when desired or in sufficient quantities because of a lack of market participants. In extreme cases, there may be no buyers or sellers at all for a particular financial instrument, making it impossible to liquidate a position.
Operational Risk
Operational risk refers to the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, and systems, or from external events. This includes risks from fraud, trading errors, legal risks, and risks related to information technology.
Risk Management in Trading
Risk management is a crucial aspect of successful trading. It involves identifying, assessing, and taking measures to reduce or mitigate the risks associated with trading. This can include setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, diversifying a trading portfolio, and continually monitoring and adjusting trades as necessary.
The Importance of Testing Trading Strategies
Before implementing a trading strategy, it’s crucial to thoroughly test it to understand its potential risks and rewards. This can be done through backtesting, which involves applying the strategy to historical market data to see how it would have performed. While backtesting has its limitations, it can provide valuable insights into a strategy’s potential performance and risk.
Conclusion
Trading reversals can be a highly profitable strategy if executed correctly. By understanding reversals, identifying liquidity grabs, marking your entry points accurately, and maintaining a good risk-reward ratio, you can maximize your profits. Remember, the key is to keep improving your strategy, use technology to your advantage, and always be aware of the risks involved. With the right approach and mindset, you can master the art of trading reversals.
Ainu Token aims to offer impartial and trustworthy information on cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and shares. However, we don't provide financial advice and recommend users to conduct their own studies and thorough checks.

Comments (No)