In an unexpected turn of events, the stock market is currently experiencing a Mania rally, marking the best half for the NASDAQ 100 ever. This surge is happening amidst talks of a recession, inflation, and a declining economy. It’s a paradox that has left many scratching their heads. The stock market, typically a barometer of economic health, seems to be defying the odds. Despite the gloomy economic forecasts and the looming threat of inflation, investors seem to be in a buying frenzy, pushing the NASDAQ to record highs. This phenomenon raises several questions about the underlying factors driving this rally and the potential implications for the broader economy.
The Three Promises That Ignited the Rally
The rally was set into motion by three promises that sparked optimism in the stock market. These were the reopening of China, the end of quantitative tightening by central banks, and the promise of advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI). However, these promises are now being put to the test. Each of these promises represented a significant potential catalyst for economic growth and investment returns. The reopening of China, for instance, signaled a return to normalcy in the world’s second-largest economy, which could boost global trade and investment. The end of quantitative tightening suggested a more accommodative monetary policy environment, which could stimulate economic activity. The promise of AI, on the other hand, represented a potential technological revolution that could drive productivity and economic growth.

China’s Reopening: A Promise Challenged
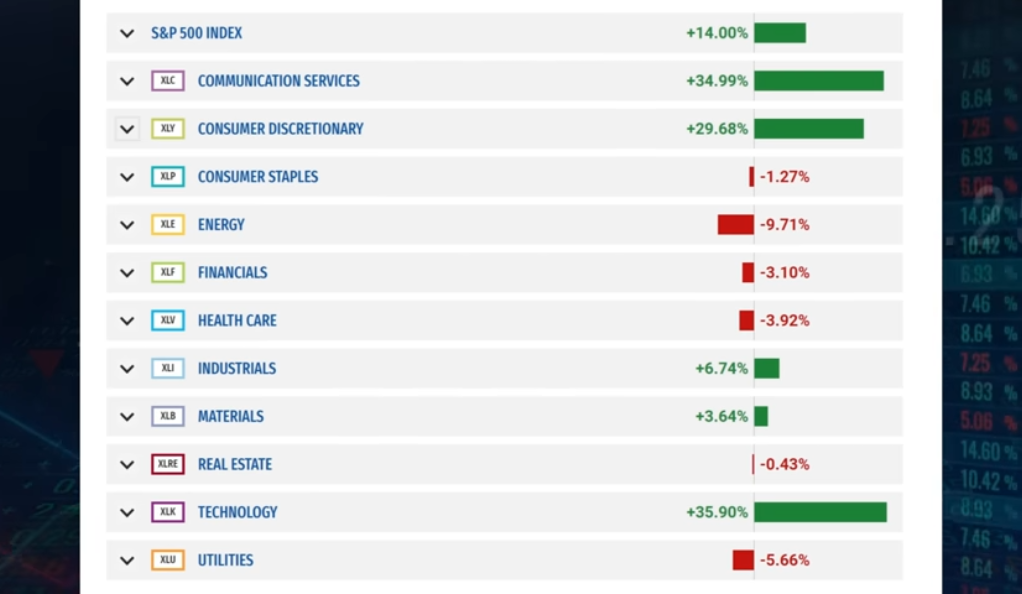
The first promise, the reopening of China, has already been challenged. Poor economic data from China has cast a shadow over this promise, causing some to question its validity. The once-inclusive rally that saw sectors such as energy, metals, industrials, and international consumer brands rallying higher has now become more selective. The Chinese economy, once a beacon of growth and stability, has been hit by a series of economic shocks, including a slowing property market, regulatory crackdowns on key sectors, and the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. These developments have raised doubts about the sustainability of China’s economic recovery and its ability to drive global growth.
AI and Quantitative Tightening: Promises Under Scrutiny
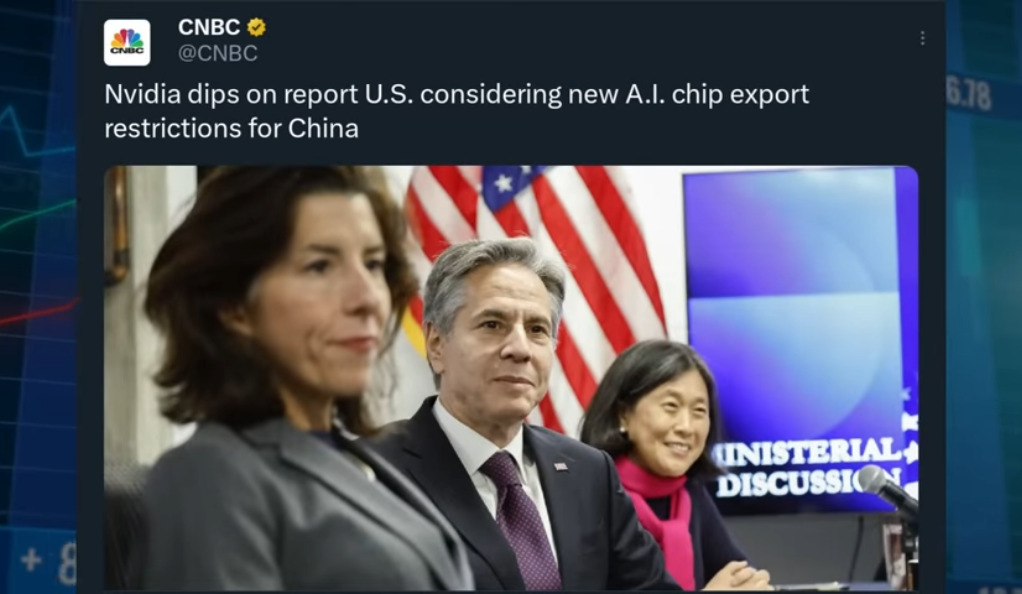
The other two promises are also under scrutiny. AI chips may be included in export restrictions to China, which could limit their potential. Central banks are also indicating that they will raise rates higher as inflation is still too high. These developments have raised questions about the sustainability of the rally. The potential restrictions on AI chip exports to China could hamper the growth of the AI industry, which has been touted as a key driver of future economic growth. Meanwhile, the prospect of higher interest rates could dampen economic activity and weigh on stock market performance.
Re-Inflation: A New Economic Phenomenon
Adding to the complexity of the situation are hints of re-inflation in the economy. Home sales and mortgage demand are increasing, and financial conditions are loosening. This is increasing the possibility of re-inflation, a phenomenon that could have significant implications for the economy. Re-inflation refers to a period of rising prices following a period of low inflation or deflation. This can occur when economic activity picks up after a downturn, leading to increased demand for goods and services. While re-inflation can be a sign of a healthy, growing economy, it can also lead to higher inflation if not managed properly. This is a delicate balancing act for policymakers, who must navigate the fine line between stimulating economic growth and keeping inflation in check.

Biden’s Economic Handling: A Point of Contention
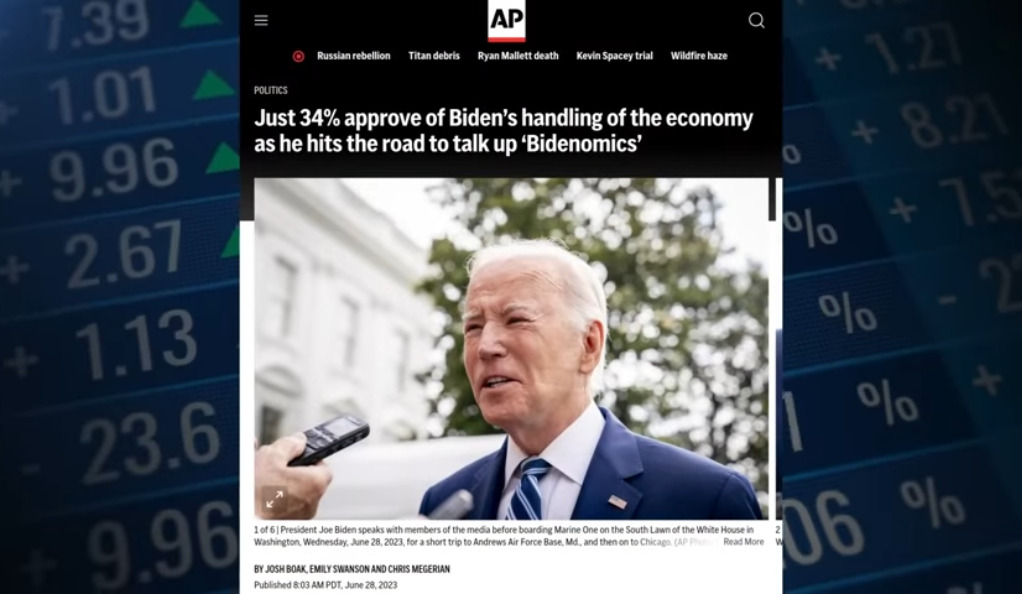
President Biden’s handling of the economy is facing criticism, with just 34% approving of his handling of the economy. His administration’s record on job creation is also being questioned. This has led to a growing sense of dissatisfaction and uncertainty among the public. Despite the administration’s efforts to stimulate the economy through fiscal stimulus and infrastructure spending, many Americans are feeling the pinch of higher living costs and stagnant wages. The administration’s handling of key economic issues, including inflation, the labor market, and the housing market, has come under scrutiny. This has led to a growing sense of dissatisfaction among the public, who are looking for concrete solutions to these pressing issues.
Central Bankers: The Guardians of the Economy
Central bankers are indicating that they will raise rates higher for longer. This is due to inflation being in charge, and they are being data-dependent. This stance by central bankers is a clear indication of their commitment to stabilizing the economy. Central bankers play a crucial role in managing the economy. By adjusting interest rates, they can influence the cost of borrowing, the rate of inflation, and the overall pace of economic activity. In the current environment, central bankers are faced with the challenging task of reining in inflation while supporting economic recovery. This requires a delicate balancing act, as raising rates too quickly could choke off economic growth, while moving too slowly could let inflation spiral out of control.
Chairman Powell: The Man at the Helm
Chairman Powell of the Federal Reserve has indicated that there will be two more rate hikes, but has not specified when these will occur. He also stated that he does not see a recession happening, a statement that has sparked debate among economists. As the head of the U.S. central bank, Powell’s words carry significant weight. His optimistic outlook on the economy, despite the looming threat of inflation, suggests a degree of confidence in the Fed’s ability to manage these challenges. However, his comments have also raised questions about the Fed’s policy trajectory and its potential impact on the economy.

The Bank of Japan: A Different Challenge
The Bank of Japan is facing a different problem, with the yen weakening due to their policy being different from other banks. They are monitoring the situation carefully, a sign of the challenges they face in managing their economy. Unlike other central banks, which are grappling with inflation, the Bank of Japan is dealing with the opposite problem: deflation. This has led to a different policy approach, with the Bank of Japan maintaining a loose monetary policy to stimulate economic activity and ward off deflation. However, this has also led to a weakening of the yen, which could have implications for the Japanese economy.
The Trajectory of Inflation: A Key Economic Indicator
The trajectory of inflation is a critical factor influencing the global economy and, by extension, the stock market. Inflation, simply put, is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising. It erodes purchasing power as each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services.
In the current economic climate, inflation has taken center stage. Central banks worldwide, including the Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan, are closely monitoring inflation rates. Their monetary policies, such as interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing measures, are largely designed to keep inflation within a manageable range.
The trajectory of inflation is influenced by a multitude of factors. One of the most significant is the movement of the dollar. As the world’s primary reserve currency, fluctuations in the value of the dollar can have far-reaching impacts on global inflation rates. A stronger dollar can suppress inflation by making imported goods cheaper, while a weaker dollar can stoke inflation by making imports more expensive.
Central banks’ actions also play a crucial role in shaping the trajectory of inflation. By adjusting interest rates and implementing other monetary policies, they can influence the rate of economic activity and, consequently, the rate of inflation. For instance, raising interest rates can slow economic activity and curb inflation, while lowering rates can stimulate economic activity and potentially lead to higher inflation.
In the current economic environment, the trajectory of inflation is uncertain. Factors such as supply chain disruptions, labor market dynamics, and fiscal and monetary policies are all influencing inflation rates in complex ways. As such, the path of inflation will be a key factor to watch in the coming months, as it will have significant implications for the economy, the stock market, and monetary policy.
Conclusion
The current stock market rally, despite the economic uncertainty, is a complex phenomenon shaped by a multitude of factors. From the promises that ignited the rally to the actions of central banks and the economic policies of world leaders, each plays a role in shaping the trajectory of the stock market. As we navigate these uncertain times, understanding these dynamics can provide valuable insights into the potential future direction of the economy and the stock market.
Ainu Token aims to offer impartial and trustworthy information on cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and shares. However, we don't provide financial advice and recommend users to conduct their own studies and thorough checks.



Comments (No)